13 Mar, 2022
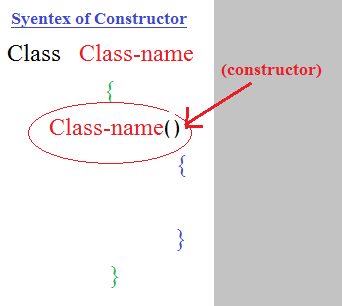
class cat {
int age; String color;
/*নিচের ক্যাট ফাংশনটি হলো কন্সট্রাক্টর (constructor)*/
cat(){
age=1; color="white";
}
void output()
{
System.out.println("age="+age+" And color="+color);
}
}
class pat
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
cat ref=new cat();
ref.output();
/*দেখার বিষয়, ref অবজেক্ট দিয়ে cat() ফাংশনকে কল করা হয়নি কিন্তু output() ফাংশনকে কল করা হয়েছে। */
}
}


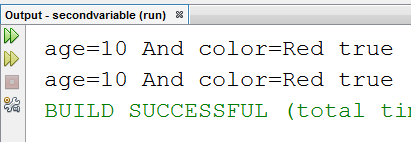
public class X {
int age; String color; boolean c;
X(){
age=10; color="Red"; c=true;
System.out.println("age="+age+" And color="+color+" "+c);
}
void output()
{
System.out.println("age="+age+" And color="+color+" "+c);
}
}
class Y{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
X ref=new X();
ref.output();
}
}

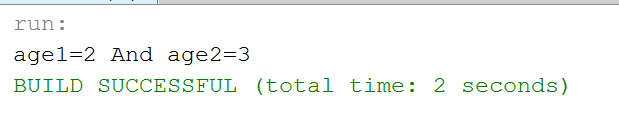
public class para {
int age1,age2;
para(int a, int b){
age1=a; age2=b;
}
void output()
{
System.out.println("age1="+age1+" And age2="+age2);
}
}
class B{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
para ref=new para(2,3);
ref.output();
}
}

public class cop {
int a; String b;
cop()
{
a=1971; b="Bangladesh";
System.out.println(a+" in "+b);
}
cop(cop ref)
{
int y=ref.a;
String x=ref.b;
System.out.println(y+" in "+x);
}
}
class Co{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
cop r=new cop();
cop r2=new cop(r);
}
}

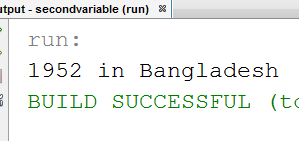
public class priv {
int a; String b;
private priv(){
a=1952; b="Bangladesh";
System.out.println(a+" in "+b);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
priv p=new priv();
}
}
/*n ot allow othaer class*/
//class Co1{
// public static void main(String[] args)
// {
// priv p=new priv();
// }
//}